Global Alzheimer’s Cases Projected to Reach
153 Million by 2050
Too Little, Too Late!
Imagine if we didn’t treat heart disease until someone had a heart attack.


Too Little, Too Late!

Imagine if we didn’t treat heart disease until someone had a heart attack.
We must intervene early and often
to avert the Alzheimer's crisis
315 Million People
have Alzheimer’s starting silently in their brains
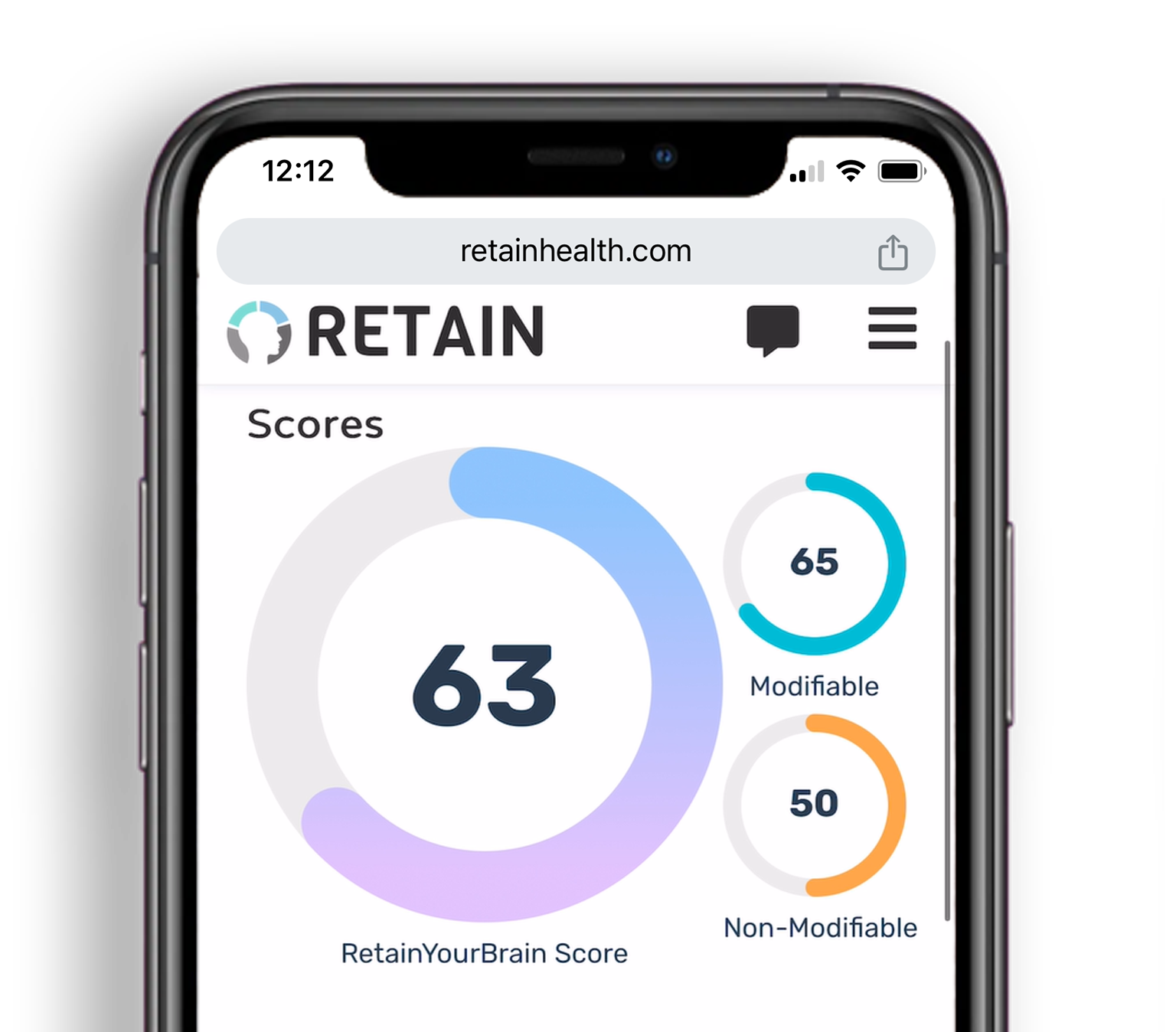
Early Intervention
could prevent or delay nearly half of dementia cases
Identify & Address
modifiable risk factors to help slow or avoid the disease
Impact on the Family


With cases expected to triple by 2060, Alzheimer’s creates profound hardship for individuals and families:
Loss of Independence
Declining thinking skills gradually make daily tasks unsafe or impossible
Strained Relationships
High stress, difficult emotions, and social isolation are rampant
Tolls on Well Being
Family caregivers are at higher risk of illness, including depression and dementia
0th
0%
0%
0x
'Even the smallest of changes can make a difference–and we owe it to our loved ones, our communities, but most of all ourselves, to try.'
— World Alzheimer’s Report 2023: Reducing Dementia Risk, Alzheimer’s Disease International
Economic Impact


On the Taxpayer
Medicare spends 3x more per person with Alzheimer’s; Medicaid spends 23x more
On Corporations
Rising unpaid Alzheimer’s caregiving disrupts work and productivity
On Families
Families bear 70% of the total lifetime cost of dementia care
0Million
0Billion
0Billion
0Million
'It’s going to bankrupt Medicare if we don’t do something about it.'
— Matthew Baumgart, Alzheimer's Association
Drug Treatment Limitations


Pharma Advancements
Pharmaceutical breakthroughs have led to first-in-kind medications targeting Alzheimer’s underlying pathology.
Amyloid-Targeting Medications
FDA-approved donanemab-azbt (Kisunla, 2024), lecanemab (Leqembi, 2023) and aducanemab (Aduhelm, 2021, discontinued in 2024) were shown to reduce brain amyloid deposits, a main feature of Alzheimer’s, and slow disease progression.
Promising, yes. But these drug therapies have significant limitations:
Cost
At $25k+/year, immunotherapies have ``low long-term value`` (ICER, 2024)
Side Effects
Require close monitoring and brain imaging; amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) include brain swelling and bleeding
Reach
Fewer than 17% of those with early-stage AD meet eligibility criteria for anti-amyloid drugs
Effectiveness
These drugs can slow symptom progression but do not stop, reverse, or cure Alzheimer’s
Lifestyle Challenges


Awareness
Prevention should begin early but adults fail to link lifestyle and risk
Access
With few Alzheimer’s prevention clinics and little primary-care training, millions lack access to care
Cost
Specialty care is expensive; many uninsured avoid even primary care
Adherence
Behavior change is a long, challenging process, especially for higher-risk populations
'Effective interventions exist, but they are not delivered at scale to everyone that would benefit from them.'
— Dementia Prevention, Intervention and Care: 2024 Report of the Lancet Commission
Impact on the Family

With cases expected to triple by 2060, Alzheimer’s creates profound hardship for individuals and families:
Loss of Independence
Declining thinking skills gradually make daily tasks unsafe or impossible
Strained Relationships
High stress, difficult emotions, and social isolation are rampant
Tolls on Well Being
Family caregivers are at higher risk of illness, including depression and dementia
0th
0%
0%
0x
'Even the smallest of changes can make a difference–and we owe it to our loved ones, our communities, but most of all ourselves, to try.'
— World Alzheimer’s Report 2023: Reducing Dementia Risk, Alzheimer’s Disease International
Economic Impact

On the Taxpayer
Medicare spends 3x more per person with Alzheimer’s; Medicaid spends 23x more
On Corporations
Rising unpaid Alzheimer’s caregiving disrupts work and productivity
On Families
Families bear 70% of the total lifetime cost of dementia care
0Million
0Billion
0Billion
0Million
'It’s going to bankrupt Medicare if we don’t do something about it.'
— Matthew Baumgart, Alzheimer's Association
Drug Treatment Limitations

Pharma Advancements
Pharmaceutical breakthroughs have led to first-in-kind medications targeting Alzheimer’s underlying pathology.
Amyloid-Targeting Medications
FDA-approved donanemab-azbt (Kisunla, 2024), lecanemab (Leqembi, 2023) and aducanemab (Aduhelm, 2021, discontinued in 2024) were shown to reduce brain amyloid deposits, a main feature of Alzheimer’s, and slow disease progression.
Promising, yes. But these drug therapies have significant limitations:
Cost
At $25k+/year, immunotherapies have ``low long-term value`` (ICER, 2024)
Side Effects
Require close monitoring and brain imaging; amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) include brain swelling and bleeding
Reach
Fewer than 17% of those with early-stage AD meet eligibility criteria for anti-amyloid drugs
Effectiveness
These drugs can slow symptom progression but do not stop, reverse, or cure Alzheimer’s
Lifestyle Challenges

Awareness
Prevention should begin early but adults fail to link lifestyle and risk
Access
With few Alzheimer’s prevention clinics and little primary-care training, millions lack access to care
Cost
Specialty care is expensive; many uninsured avoid even primary care
Adherence
Behavior change is a long, challenging process, especially for higher-risk populations